Building on our introduction to Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) and their transformative effects on software architecture, this second article in the “Emerging Technologies and Their Impact” series will provide a deeper technical exploration. We will examine specific architecture models and patterns, and offer visual aids to enhance understanding and implementation.
📖 Architectural Models for AI and ML Integration
1. Microservices Architecture
Microservices architecture, known for its flexibility and scalability, offers an ideal framework for integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) into existing systems. This architecture decomposes complex applications into smaller, independent services, each running its own process and communicating with lightweight mechanisms, often an HTTP resource API.
This modular nature allows each component, such as an AI-driven service, to scale independently according to its specific resource demands without affecting the overall system. This is particularly beneficial for deploying resource-intensive ML models, which may require more computational power as they scale or as the complexity of tasks increases.
Component-Based Development
In a microservices architecture, applications are built as a collection of components or services that are developed, deployed, and operated independently. For AI and ML integration, this means that individual components like data preprocessing, model training, and real-time inference can be managed as separate microservices. Each service can be updated or replaced without re-deploying the entire application, facilitating faster updates and better management of dependencies.
Example of AI/ML Service Integration
Consider a retail e-commerce platform that uses ML for personalized product recommendations. Here’s how AI and ML components might integrate into a microservices architecture:
User-Management Service: Handles user authentication and profile management.
Data Processing Service: Gathers user behavior data and prepares it for analysis.
ML Model Service: Receives processed data from the Data Processing Service. It runs the ML algorithms that generate personalized product recommendations based on user behavior.
Business-Logic Service: Uses the recommendations from the ML Model Service to tailor the user interface dynamically, showing personalized product recommendations.
These services communicate via RESTful APIs, with each service maintaining its own database, thereby decentralizing data management and enhancing the system’s resilience and scalability.
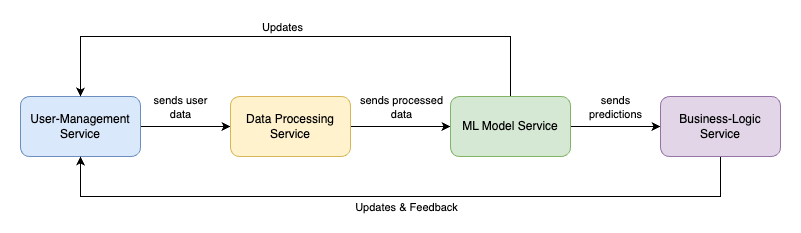
Diagram created by the Author
This diagram not only shows the modular interaction but also highlights how feedback from the Business-Logic Service can be used to update the ML models, enabling continuous learning and improvement based on real-time user interactions.
Scaling ML Models
When an ML model requires more resources due to increased data volume or complexity, the corresponding service can be scaled independently. For instance, if the ML Model Service in our e-commerce platform needs to handle more data during a sales event, it can be scaled up dynamically using container orchestration tools like Kubernetes, which manages the deployment, scaling, and operations of containerized applications across clusters of hosts.
By examining microservices through this detailed lens, architects and developers gain a clear understanding of how AI and ML can be seamlessly integrated into scalable, efficient, and robust systems, facilitating rapid deployment and greater innovation in software solutions.
“The question isn’t whether AI will change the world, but how and when. Those who understand it and can work with it will drive progress.” — Eric Schmidt
2. Serverless Architecture
Serverless computing represents a paradigm shift in how applications are built and scaled, offering a way to abstract server management and infrastructure decisions away from the app development process. This model is particularly well-suited for AI and ML deployments because it can dynamically allocate computational resources based on the demand of specific AI tasks. This is ideal for scenarios where the workload can be highly variable, such as sporadic data processing tasks or on-demand ML model inference.
Event-Driven Execution
Serverless architecture is inherently event-driven, typically executing code in response to various events, including HTTP requests, file uploads, queue operations, or in-app activity. For AI and ML, this means that functions are only run when needed, such as processing an image uploaded by a user for real-time object recognition, and are idle at other times, which can significantly reduce costs.
Scalability and Cost-Effectiveness
When an ML model is deployed in a serverless environment, the serverless platform automatically scales up to process an incoming request, be it for a single file analysis or thousands of simultaneous analyses, and scales down as soon as the job is done. This elasticity allows developers to handle high loads without paying for idle computing resources.
Use Case Example: Real-Time Image Processing
Imagine an application that provides real-time image recognition to identify objects in uploaded photographs. Here’s how serverless architecture supports this process:
User Uploads an Image: This triggers an event.
Invoke ML Model: The serverless function is invoked, which loads the ML model into memory, processes the uploaded image, and identifies objects in the image.
Return Results: The results are sent back to the user’s device.
Resources Released: Upon completion, computational resources are released, minimizing ongoing costs.
This use case illustrates not only the responsiveness of serverless architecture but also its efficiency in managing resource use and minimizing operational costs.

Diagram created by the Author
By understanding these enhanced characteristics of serverless architecture, developers and architects can better utilize this model for deploying AI and ML tasks that are cost-effective, scalable, and highly responsive to user interactions and data inputs. This architectural approach not only simplifies the management of variable AI workloads but also optimizes operational efficiency and performance.
Conclusion
Architects can effectively integrate AI and ML into their systems by understanding and applying appropriate architectural patterns, such as microservices or serverless. This deep dive aims to equip solution architects with the knowledge to leverage AI and ML technologies to their full potential. As we continue to explore emerging technologies in subsequent articles, remember that the key to successful integration lies in both technical understanding and strategic implementation.